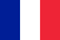
Onychomycosis of the feet and hands is characterized by a variety of symptoms. How the nail fungus looks depends on the type of pathogen (there are about 50 in total), the localization of the main infection and the corresponding disease. There are some of the most common types of onychomycosis, which have their own characteristics. Identification of pathology at an early stage makes it possible for treatment only with the help of local funds. If not, you need to take systemic antimycotics. With further forms of the disease and total damage, recovery of the nail plate becomes impossible.
Onychomycosis: a brief description
Onychomycosis is a fungal infection of the nails on the feet (in 80% of cases) or on the hands. At risk are the elderly (of which 40% of people over the age of 60 are sick), as well as those suffering from pathologies such as:
- psoriasis;
- diabetes mellitus (prevalence three times higher than other population groups) and other endocrine diseases;
- violation of blood supply to the extreme part due to cardiovascular pathology, the process of elimination of blood vessels, causing their narrowing; angiotrophoneurosis, varicose veins;
- oncological diseases;
- hemorrhagic sarcomatosis (various skin cancers);
- dermatosis associated with violations of the process of cell keratinization, ichthyosis;
- broken bones of hands or feet;
- other serious somatic diseases, which cause general fatigue and decreased body defenses.
The following expertise belongs to the occupational risk group:
- miners;
- athlete;
- employees of public institutions;
- metallurgist;
- members of the military;
- medical workers;
- industrial worker;
- cooks and other workers whose activities are related to frequent contact with water.
Among all nail diseases, onychomycosis is in third place in terms of prevalence, and the number of people who become carriers of this disease is one -fifth of the world’s population. The danger of this disease lies in the fact that the focus of a fungal infection can exist for a long time and be an active source for infecting others, including your own family members.
In addition, the fungus causes general sensitization of the body due to the production of toxins, which contributes to the development of allergic and dermatological diseases in patients. Therefore, it is important to identify the fungus at an early stage and stop its growth, which spreads through the lymph and blood. Infection occurs in the following ways:
- in public places such as baths, saunas, swimming pools, gyms;
- through shared household items (carpets, wipes, towels);
- during nail polish treatment;
- while wearing other people’s shoes.
Risk factors also:
- wear tight shoes;
- humid and hot climate;
- increased foot sweat;
- weakened immunity;
- taking hormone and antibacterial medications;
- injuries and dystrophic changes in the nail plate.
Varieties of this disease
There are several types of onychomycosis, which are classified according to several criteria. These features help determine the appearance of nail fungus on the hands and feet.
According to the type of pathogen. Defeat of the nail plate by one type of pathogen occurs in ¾ all cases, two - in 16%, three - in 9%. Mixed infections most commonly occur in elderly patients. The most common pathogens are:
- Dermatophyte fungi, the most common being Trichophyton rubrum (80% of all cases) and mentagrophytes var. Interdigitale (about 10% of cases). Epidermophyton floccosum, T. violaceum and T. tonsurans are less common (3% of total cases).
- Yeast fungi of the genus Candida, which affect more nail plates on the hands (in 40% of cases) than on the feet. The disease is often accompanied by chronic candidiasis of the skin and mucous membranes. Some species of Candida exist as a symbiotic on the skin of healthy people.
- Non -dermatophyte molds - Scytalidium dimidiatum and hyalinum, Onychocola canadensis. Often found in countries with hot and humid climates.
According to the shape of the nail plate lesion. In the same patient, the types of damage can be combined. Depending on the changes in the nail, the following shapes are distinguished:
- Normotrophic - only discoloration (yellowing at a distance, free edges). The normal shape and thickness of the plate is maintained over a long period of time. At its edges, a thickening is formed as a result of the too rapid cleavage of horny cells under the nail.
- Hypertrophic - in addition to yellowing and dullness, thickening and deformation of the nail plate is observed. Over time, they acquire transverse streaks, becoming a dirty, loose gray color on the distal edge.
- Atropic - severe nail destruction occurs, the subungual skin is exposed and covered with a brittle and fragile mass.
- According to the type of onycholysis - there is a thinning of the nail plate, which is separated from the base of the nail. The color is dull, dirty gray or yellowish; in the root region, the color may not change.
Damage localization:
- Distal lateral onychomycosis.
- White surface. While scraping the damage, you can determine its superficial nature.
- Subungual proximal.
- Number of dystrophies.
The first type is the most common, and the source of the lesion is the infected skin. The beginning of the process takes place through the distal part - the free edge towards the root, which is why this variety gets its name. In the early stages, the nail plate retains its normal appearance, but then gradually separates from the bed and becomes yellowish. In some cases, thickening is observed. In the final stage, the nail color acquires a different color (from green and blue to brown), depending on the bacterial contamination.
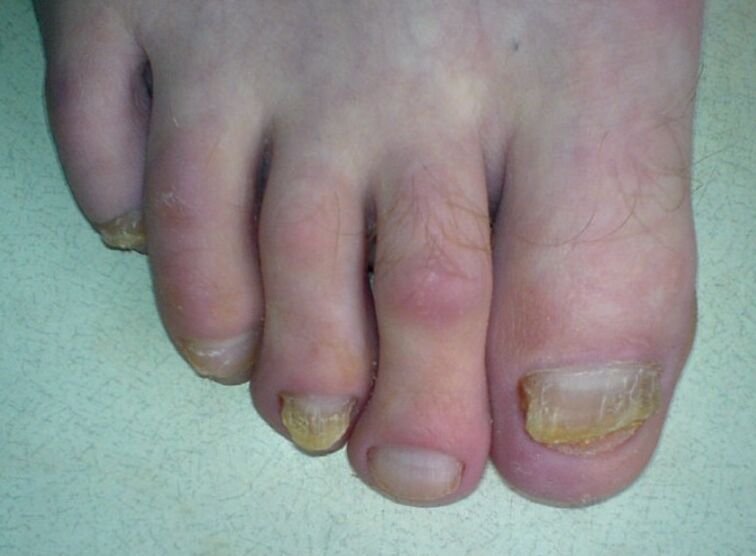
The second form of onychomycosis is characterized by the appearance of white spots, lines that appear on the outer surface of the nail and gradually spread throughout the plate. Over time, the spots change color to yellow or yellow-brown. In most cases, these lesions are associated with seeding with trichophyton mentagrophytes or molds of the genus Aspergillus. This form of the disease is more common in the elderly. The roots of the nails and beds, as a rule, remain intact, and the plates crumble and become gray or brown in color.
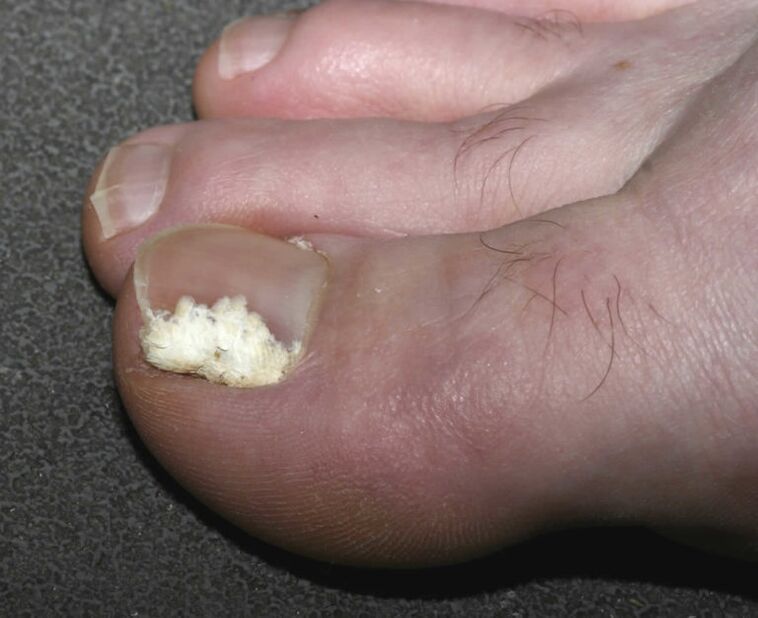
Subungual lesions are the rarest form. The causative agent can be all three types of pathogens. The spread of infection occurs from the skin or lateral ridges towards the root of the nail. The stain appears in the middle of the nail plate or in the hole, and then quickly disappears. The beds and roots of the nails are not inflamed, but secondary bacterial infections often occur, which cause the nails to darken.
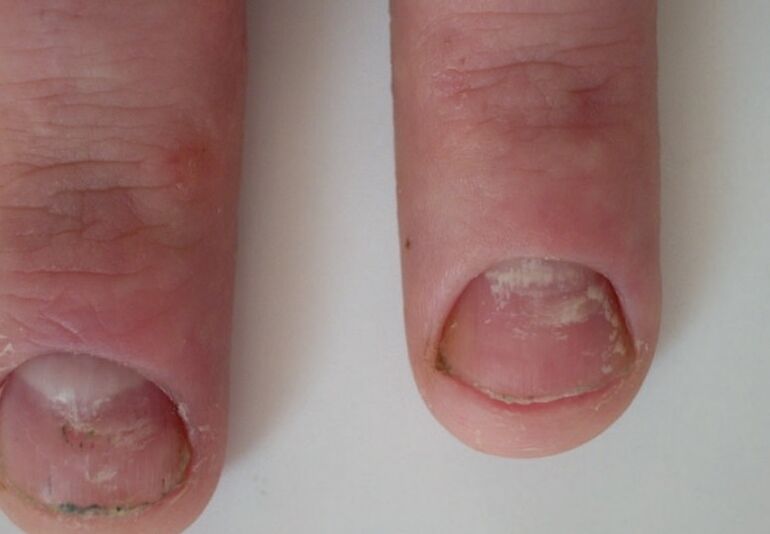
With the whole form of the disease, the whole area of the nail is affected, which in many cases is accompanied by its complete destruction. The roots disappear or thicken pathologically, resulting in abnormal plate formation. In the later stages of the disease, only the remnants of its destruction are observed. This form of onychomycosis often occurs in candidiasis. The causative agent can also be an epidermophytic fungus.
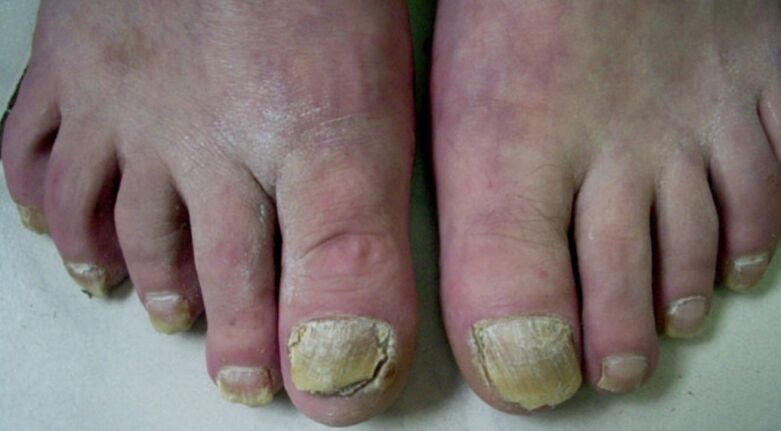
The first signs of the disease
There are symptoms that help recognize a fungal infection at an early stage. The patient may have one or more of the following:
- loss of transparency and luster on the nail plate;
- nail color becomes whitish or yellowish;
- nail edges become uneven, thin, soft;
- appearance of yellow or white spots, stripes along the edges of the plate (on the hands-in the middle of the nail plate);
- some types of fungus cause damage to the nails only on the first toe, the rest remain unchanged (these include superficial white onychomycosis, which usually damages the first toe nails, more rarely the little toes);
- the plate moves from the bed by 1-2 mm.
For a long time, the pathological process can be localized only along the distal edge of the plate, so it is possible to stop the infection by preventing deformation, release of the nail plate and damage to the roots, which leads to irreversible consequences.
During the process, other signs appear:
- white stripes flow from free edge to root;
- "Ribbing" the nail in a transverse direction;
- its thinning;
- plate flakes and other symptoms corresponding to a particular type of onychomycosis.
Superficial white onychomycosis almost never appears on the fingernails. Sometimes this form of the disease is combined with a distant form. When infected Т. rubrum, its damage is most frequent. When infected with fungi of the genus Candida (in more rare cases, with fungal infections), inflammation of the posterior or lateral nails first occurs, accompanied by the following symptoms:
- redness, compaction and swelling of the roller;
- change its shape;
- the appearance of white scales along the edges of the roller;
- cuticle separation and its destruction;
- pain at the site of the lesion on palpation;
- in rare cases, when pressed, a small amount of pus is released.
In children, the disease at an early stage is characterized by the following features:
- rough nail surface;
- its shape often does not change;
- defeat in most cases - on the far edge;
- active fungal processes are also observed on the skin of the feet;
- in more rare cases, subungual hyperkeratosis is detected.
If the nail acquires a bright green color, then this indicates the addition of a secondary bacterial infection - Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and the black color indicates an infection on the Proteus.
Differences from other pathologies
Changes in the nails, similar to onychomycosis, are also observed in other diseases:
- psoriasis (peeling of the nail along its edges, its uneven thickening, "thimble" of its surface, peeling along the ridge, yellowing, destruction of the nail);
- lichen planus (deep crack in the center of the plate, longitudinal thickening, subungual hyperkeratosis, rupture along the distal edge, increased fragility, loss of nails due to separation);
- eczema (transverse grooves, tissue softening, peeling along the edges, roller thickening);
- nail trichophytosis (in this case, there are also lesions on the smooth or hairy skin).
Since the external symptoms of onychomycosis may coincide with non -fungal diseases, microscopic examination and scattering of pathogens are required to make an accurate diagnosis.
Treatment
In the early stages of the disease, if no more than half of the nail plate is affected, treatment can be carried out only using local remedies. Therapeutic tactics also depend on the form of the disease.
Long -term onychomycosis, with bacterial complications should be treated for a longer period of time - for several months, with the help of systemic antifungal drugs. Local therapy is carried out in cases where there is a high risk of side effects, in pregnant and lactating women, in people with liver disease, kidney disease, drug allergies. The disadvantage of local remedies is that they cannot penetrate the roots of the nail and, if the matrix is damaged, such treatment is ineffective.
Before using antifungal agents, pre -treatment is required - removal of the infected area. This is done with the help of keratolytic agents: ointments, patches. Therapy is carried out in 1-3 weeks. After cleansing, apply one of the antimycotic drugs in the form of:
- cream;
- solution;
- varnish.
Creams and solutions are applied twice a day until healthy nails grow back. For preventive purposes, it is recommended to process unaffected nails. Varnish is applied 1-2 times a week for at least six months. They can be used as the only remedy for treatment only if not more than a third of the nail plate is affected, and the duration of the disease does not exceed 1 year.
If a fungal infection on the toenails, it is necessary to disinfect the shoes with 40%formalin solution. Once wiped with a damp cotton cloth, it is left in the shoe and wrapped overnight in a plastic bag. Because formalin is toxic, after disinfection should be done ventilation of shoes and rooms. The socks of the sick person must be boiled.
As a precaution, the following recommendations must be observed:
- Take steps to get rid of excessive foot sweat (use of powders, treatment with formulations based on urotropin).
- When visiting swimming pools, beaches and similar places, use individual rubber stones.
- Change socks daily, periodically disinfecting shoes.
- Treat other nail diseases in a timely manner, moisturizing the skin of dry feet and hands.
- Use your own shoes.